The term “CK NAC Reagents” refers to the reagents used in the measurement of creatine kinase (CK) activity using the N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) method. CK is an enzyme found in various tissues, including skeletal muscle, heart muscle, and brain. It is commonly measured in clinical laboratories as an indicator of muscle damage or disease.
The NAC method is one of the enzymatic methods used to measure CK activity. It involves the use of specific reagents that react with CK to produce a detectable signal, typically through the measurement of an absorbance change. The NAC method utilizes N-acetyl-L-cysteine as a substrate to initiate the enzymatic reaction.
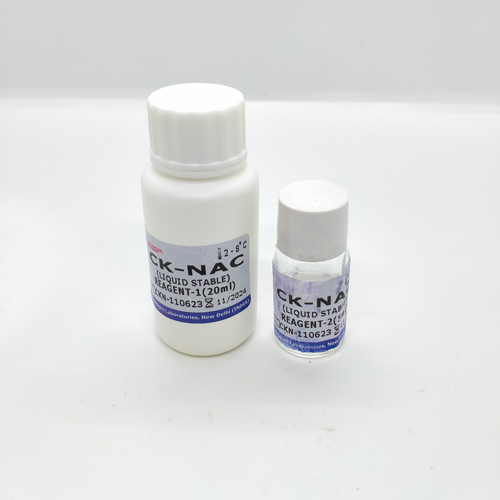
The specific composition of CK NAC reagents can vary among different manufacturers or assay kits. However, typical components of CK NAC reagents may include:
- Substrate: N-acetyl-L-cysteine, which serves as the substrate for the CK enzyme.
- Coenzyme: Some kits may include a coenzyme, such as NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, reduced form), to facilitate the reaction.
- Buffer: A buffer solution is included to maintain the optimal pH for the enzymatic reaction.
- Stabilizers and additives: Reagents may contain stabilizers and additives to enhance the stability and performance of the assay.
It’s important to note that the exact composition and formulation of CK NAC reagents may vary between different manufacturers and assay kits. Therefore, it is recommended to consult the specific instructions provided with the kit or refer to the manufacturer’s documentation for detailed information on the reagents and their proper usage.
Performing the CK NAC assay involves following the instructions provided with the kit, which typically include steps for preparing standards of known CK activity, preparing the samples, adding the CK NAC reagents, allowing the enzymatic reaction to occur, and measuring the resulting signal (e.g., absorbance) using a spectrophotometer or other suitable instrument.






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.